The Conversation Model
Turn-Based Models
- Definition of a turn (linguistics)
- Period during which one speaker holds the
floor
- Varies from interruption to several minutes
- Logical chunking for conversations
- Accumulate features within each turn
State Dependencies
- Previous turn in conversation
- Effect of what the last person said or
did
- Models reaction to others
- Previous turn by the given speaker
- Captures the state of the speaker so far
- Example: if a speaker is angry, will remain
so
Parsing a Conversation
- Learning interaction grammars
- By labeling turns, we can learn transitions
- Patterns of these turns: "conversation
type"
- Decoding conversation progress
- Info from multiple turns => the individuals'
roles
- More accurate than attempting to classify
individual turns
|
|
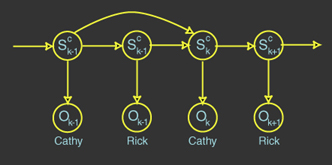
Figure 1. Conversation model showing state
dependencies
|
|
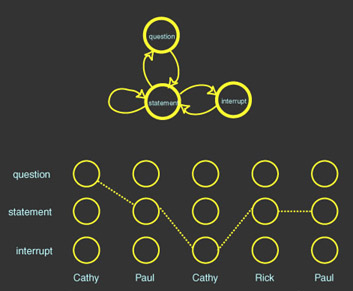
Figure 2. Interaction grammar and a parse
of the conversation
|
|