

Next: The Signals
Up: Quantifying Driver Stress: Developing
Previous: Capturing Context
In both pilot experiments, the drivers wore physiological sensors under
his or her clothing while driving. The sensors were placed so as not to
restrict the motion of the arms, the hands or the foot responsible for
control of the gas and the brake. The placement of the sensors in the first
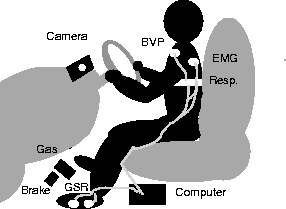
pilot is shown in Figure 5. For the second pilot an EKG
was placed on chest as shown in Figure 6 and the BVP
was instead placed on the middle finger.
Figure:
A diagram showing how the physiological sensors were worn by
the driver in the first pilot study. The skin conductance sensor
(GSR) was placed on the arch of the left foot. The respiration sensor
was placed over the diaphragm. The electromyogram (EMG) was placed on the
trapezius muscle on the left shoulder. In the first pilot, the BVP
was paced on the driver's torso to avoid motion artifacts as shown. In the
second pilot, an EKG was worn on the chest and the BVP was carefully
placed on the driver's finger.
 |


Next: The Signals
Up: Quantifying Driver Stress: Developing
Previous: Capturing Context
Jennifer Healey - fenn@media.mit.edu
1999-02-12

