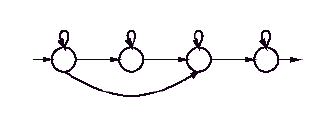
The initial topology for an HMM can be determined by estimating how
many different states are involved in specifying a sign. Fine tuning
this topology can be performed empirically. In this case, an initial
topology of 5 states was considered sufficient for the most complex
sign. To handle less complicated signs, skip transitions were
specified which allowed the topology to emulate a strictly 3 or 4
state HMM. While different topologies can be specified per sign
explicitly, the above method allows training to adapt the HMM
automatically without human intervention. However, after testing
several different topologies, a four state HMM with one skip
transition was determined to be appropriate for this task (Figure
1).