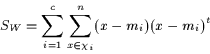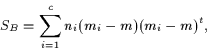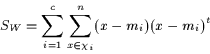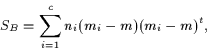Next: Summary
Up: Digital Processing of Affective
Previous: Feature Extraction
The techniques to discriminate states based on the eleven features
used a Fisher linear discriminant projection [7] and the
leave one out test method. For each trial, a single point, x, was
excluded from the data set and a Fisher projection matrix,
W was calculated for remaining members of the set. The
excluded point was then projected using W and classified
using quadratic and linear classifiers, in the standard method
described by Therrien [8].
The Fisher projection matrix which in some sense maximizes the ratio
of the between-class
scatter, SB, to the within class scatter, SW [7],
where these matrices are defined as:
given c is the number of classes, ni is the number of sample
vectors in a class, mi is the sample mean for class i, m is
the total mean, and
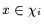 are the 11-dimensional feature
vectors comprising class i. The Fisher projection matrix is the
matrix W whose columns, wi correspond to the largest eigenvalues
in:
are the 11-dimensional feature
vectors comprising class i. The Fisher projection matrix is the
matrix W whose columns, wi correspond to the largest eigenvalues
in:
This matrix is then used to project the test point onto the classifier
space using
The results of the recognition on a number of subsets of data are
reported in Table 3. The discrimination is best
between anger and a set of more peaceful emotions containing the classes:
no emotion, love and reverence. The entire set of eight emotion
classes can also be well separated into two categories: high arousal
containing anger, grief, romantic love and joy, and low arousal
containing no emotion, hate, love and reverence. However, no good
discrimination was found for positive valence vs. negative valence
emotions.
Figure:
Anger is well separated from more peaceful emotions, in this
example the states of No Emotion, Love and Reverence make up the set
of peaceful states
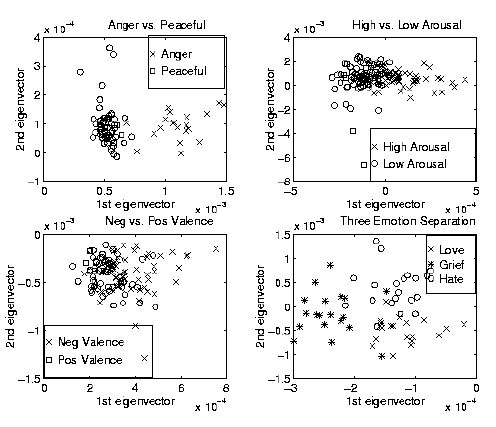 |
Table:
The results of discriminating between subsets of emotions.
For these results the peaceful class contains no emotion,
reverence, and love; the aroused class contains anger,
grief, romantic love, and joy; the calm class contains no
emotion, hate, love, and reverence; the positive valence class
contains love, romantic love, and joy, and the negative valence class
contains anger, hate, and grief. Anger was most easily distinguished,
and good discrimination was achieved for the high vs. low arousal
states. Positive and negative valence were not well separated.
Emotion |
Set |
Linear |
Quadratic |
| Set |
Size |
error |
correct |
error |
correct |
| anger |
20 |
2 |
90% |
0 |
100% |
| peaceful |
60 |
1 |
98% |
1 |
98% |
| high arousal |
80 |
15 |
81% |
16 |
80% |
| low arousal |
80 |
11 |
86% |
10 |
88% |
| positive |
60 |
15 |
75% |
11 |
82% |
| negative |
60 |
29 |
53% |
30 |
50% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Although specific patterns were not found to discriminate all eight
emotions, certain subsets of three emotions could be well separated
as shown in Table 4.



Next: Summary
Up: Digital Processing of Affective
Previous: Feature Extraction
Jennifer Healey - fenn@media.mit.edu
1999-02-11