 |
Muscle activity has been shown to increase during
stress[CT90]. People may unconsciously clench their
muscles in a state of mental stress even when no physical activity is
required[DEM88]. Firing from this muscle could indicate either
unconscious clenching due to stress or firing due to motion, such as
turning the car. Data from the context sensors can be used to
differentiate these reactions. In the pilot experiment, the EMG was
placed on the trapezius muscle. The EMG signal was sampled 20Hz in the first
experiments which resulted in signal aliasing. Therefore, only a rough
approximation of the muscle activity could be extracted. The muscle
activity trigger first smoothed using a low-pass filter, then
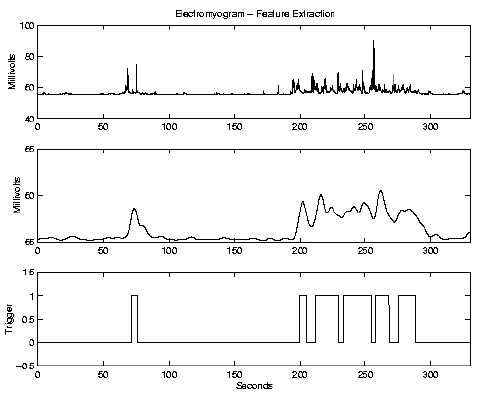
applied a threshold. Figure
10 shows the raw signal, the smoothed signal and the
results of the threshold trigger.
 |