

| External Interfaces/API |   |
Complex Double-Precision Matrices
The most common data type in MATLAB is the complex double-precision, nonsparse matrix. These matrices are of type double and have dimensions m-by-n, where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns. The data is stored as two vectors of double-precision numbers - one contains the real data and one contains the imaginary data. The pointers to this data are referred to as pr (pointer to real data) and pi (pointer to imaginary data), respectively. A real-only, double-precision matrix is one whose pi is NULL.
Numeric Matrices
MATLAB also supports other types of numeric matrices. These are single-precision floating-point and 8-, 16-, and 32-bit integers, both signed and unsigned. The data is stored in two vectors in the same manner as double-precision matrices.
MATLAB Strings
MATLAB strings are of type char and are stored the same way as unsigned 16-bit integers except there is no imaginary data component. Unlike C, MATLAB strings are not null terminated.
Sparse Matrices
Sparse matrices have a different storage convention than full matrices in MATLAB. The parameters pr and pi are still arrays of double-precision numbers, but there are three additional parameters, nzmax, ir, and jc:
nzmax is an integer that contains the length of ir, pr, and, if it exists, pi. It is the maximum possible number of nonzero elements in the sparse matrix.
ir points to an integer array of length nzmax containing the row indices of the corresponding elements in pr and pi.
jc points to an integer array of length N+1 that contains column index information. For j, in the range 0 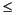
j 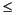
N-1, jc[j] is the index in ir and pr (and pi if it exists) of the first nonzero entry in the jth column and jc[j+1] - 1 index of the last nonzero entry. As a result, jc[N] is also equal to nnz, the number of nonzero entries in the matrix. If nnz is less than nzmax, then more nonzero entries can be inserted in the array without allocating additional storage.
Cell Arrays
Cell arrays are a collection of MATLAB arrays where each mxArray is referred to as a cell. This allows MATLAB arrays of different types to be stored together. Cell arrays are stored in a similar manner to numeric matrices, except the data portion contains a single vector of pointers to mxArrays. Members of this vector are called cells. Each cell can be of any supported data type, even another cell array.
Structures
A 1-by-1 structure is stored in the same manner as a 1-by-n cell array where n is the number of fields in the structure. Members of the data vector are called fields. Each field is associated with a name stored in the mxArray.
Objects
Objects are stored and accessed the same way as structures. In MATLAB, objects are named structures with registered methods. Outside MATLAB, an object is a structure that contains storage for an additional classname that identifies the name of the object.
Multidimensional Arrays
MATLAB arrays of any type can be multidimensional. A vector of integers is stored where each element is the size of the corresponding dimension. The storage of the data is the same as matrices.
Empty Arrays
MATLAB arrays of any type can be empty. An empty mxArray is one with at least one dimension equal to zero. For example, a double-precision mxArray of type double, where m and n equal 0 and pr is NULL, is an empty array.
 | Data Storage | Using Data Types |  |